Selecting the right WordPress theme is one of the most critical decisions you can make when building your website. A WordPress theme determines the design, layout, and even the functionality of your website. Choosing the perfect theme sets the tone for your brand, enhances user experience, and can significantly impact your website’s performance and SEO ranking.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about how to pick the best WordPress theme for your website. From key factors to consider to common mistakes and expert tips, this blog will ensure you make an informed decision that aligns with your goals.
Introduction
A WordPress theme is essentially a template that dictates how your website will look and function. It controls the visual elements like colors, fonts, layouts, headers, and footers while determining the user experience on your site. Themes are vital because they not only influence aesthetics but also functionality, performance, and user engagement.
Choosing the right theme for your WordPress website is about more than just looks. The right choice ensures that your website runs smoothly, supports the features you need, and provides a seamless experience for visitors.
In this blog, we’ll guide you through the entire process of selecting a WordPress theme. By the end, you’ll understand how to prioritize design, performance, compatibility, and SEO features to ensure your WordPress website stands out.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a WordPress Theme
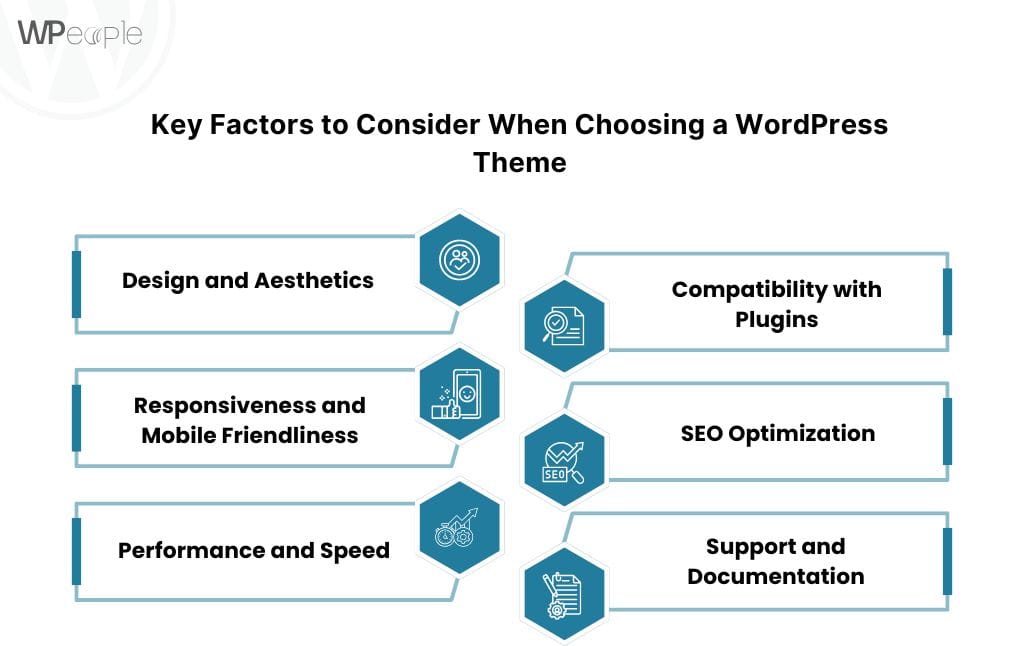
When choosing a WordPress theme, several critical factors should guide your decision. These will help you select a theme that aligns with your brand’s vision, supports essential features, and is easy to maintain in the long term.
Design and Aesthetics
Your WordPress theme should reflect your brand identity and resonate with your target audience. A visually appealing design creates trust and credibility with visitors.
Here are a few tips when evaluating the design:
- Prioritize Simplicity vs. Customization: Simplicity can be a better choice if you want clean, professional visuals with minimal distractions. However, if your brand requires unique branding elements, go for themes with high customization options.
- Ensure Brand Alignment: Your theme’s colors, fonts, and overall style should align with your brand’s voice.
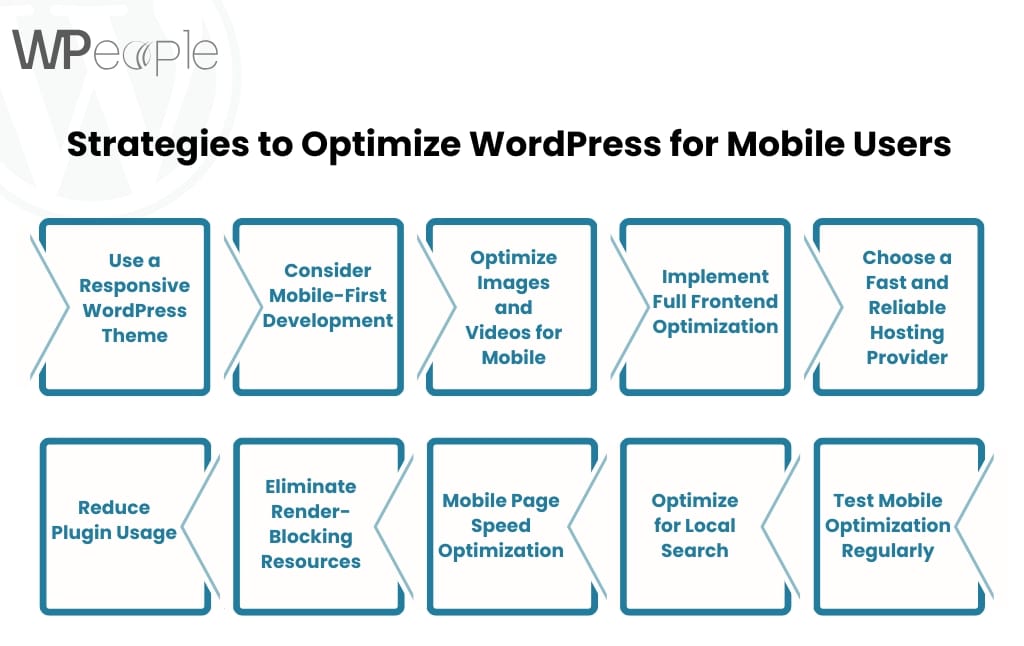
Responsiveness and Mobile Friendliness
A responsive WordPress theme is crucial in today’s mobile-first world. Mobile devices account for a majority of web traffic globally, so ensure your website looks great on smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
When evaluating responsiveness, ask:
- Does the design adjust seamlessly to different screen sizes?
- Are all buttons, menus, and content easily accessible on mobile devices?
You can test responsiveness using online tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test or by resizing your browser window during testing.
Performance and Speed
Website performance directly impacts user experience and SEO rankings. A well-coded, optimized WordPress theme ensures your website loads quickly. Websites with slow load times risk losing visitors and search rankings.
Here’s how you can ensure great performance:
- Opt for lightweight themes with minimal bloat.
- Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to assess website speed.
- Avoid themes overloaded with unnecessary features and widgets.
Compatibility with Plugins
WordPress relies on plugins for added functionality, whether you’re adding contact forms, e-commerce capabilities, SEO tools, or other features. Your WordPress theme must be compatible with the plugins you plan to use.
Before choosing a theme:
- Check if it supports popular plugins like WooCommerce, Yoast SEO, Elementor, or Contact Form 7.
- Read user reviews to confirm compatibility and ease of integration.
SEO Optimization
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) determines how well your site ranks in search engine results. A good WordPress theme should be SEO-friendly and adhere to coding best practices.
Look for these features in a WordPress theme:
- Fast load times.
- Schema markup support.
- Clean and optimized code.
If you’re unsure, many SEO plugins can help boost your site’s SEO, but a good theme will give you a head start.
Support and Documentation
Support and documentation are crucial for navigating technical challenges. A theme with detailed documentation and active support makes it easier to troubleshoot problems or make adjustments.
Here’s how you can check this:
- Look for reviews and ratings to ensure the theme provider offers excellent customer service.
- Examine whether the theme comes with comprehensive guides, tutorials, or user forums.
Types of WordPress Themes: Which One is Right for You?
WordPress themes come in different styles, functionalities, and marketplaces. Understanding the types will help you narrow down your search and choose one that fits your needs.
Free vs. Premium WordPress Themes
- Free WordPress Themes: Available directly in the WordPress repository, these themes are a great option for small websites or those on a budget.
- Pros: Free, quick to set up, and accessible.
- Cons: Limited features, fewer design options, and sometimes less reliable support.
- Premium WordPress Themes: These are paid themes that offer advanced design options, features, and customer support.
- Pros: More customization, advanced features, and dedicated support.
- Cons: Costly for small projects.
When to Invest in Premium Themes: If your website requires unique features, advanced design, or robust e-commerce capabilities, premium themes are often worth the investment.
Specialized Themes vs. Multipurpose Themes
- Specialized Themes: Designed for specific niches like blogs, e-commerce stores, portfolios, or non-profits. They cater to very specific website needs.
- Multipurpose Themes: These are versatile, all-in-one themes that can adapt to different purposes. They’re great if you plan to change your website’s direction in the future.
Theme Marketplaces to Explore
Several online marketplaces are trusted sources for premium and specialized WordPress themes:
- ThemeForest: A vast marketplace with thousands of themes suitable for all niches.
- Elegant Themes: Known for its Divi Builder and well-designed themes.
- StudioPress: Home to the Genesis Framework, perfect for advanced users.
Explore these marketplaces for inspiration and find a theme that suits your goals.
How to Assess a WordPress Theme Before Installing It
Before installing a WordPress theme, take the time to evaluate it to ensure it meets your needs.
Examine the Theme Demo
Theme demos showcase how a theme looks and works in real-time. Always test out demo sites to determine if the theme will meet your expectations.
Read Customer Reviews
Customer reviews provide insights into real user experiences. Look for consistent positive or negative feedback about a theme’s reliability, speed, and support.
Test the Theme’s Features with a Demo Site
Many theme providers allow you to use demo installations to explore features. These are invaluable for testing the user experience without fully committing.
Check for Compatibility with Your WordPress Version
Always check if the theme is updated and compatible with your current WordPress version to avoid conflicts or bugs.
Common Mistakes When Choosing a WordPress Theme & How to Avoid Them
Avoid these common pitfalls to save time and ensure you choose the right WordPress theme:
- Choosing a Theme Just for Its Look, Without Considering Functionality.
- Ignoring Mobile Responsiveness.
- Not Checking for SEO Best Practices.
- Overloading the Theme with Features You Don’t Need.
- Skipping Reviews or Not Testing the Theme in Action.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures a smoother website-building journey.
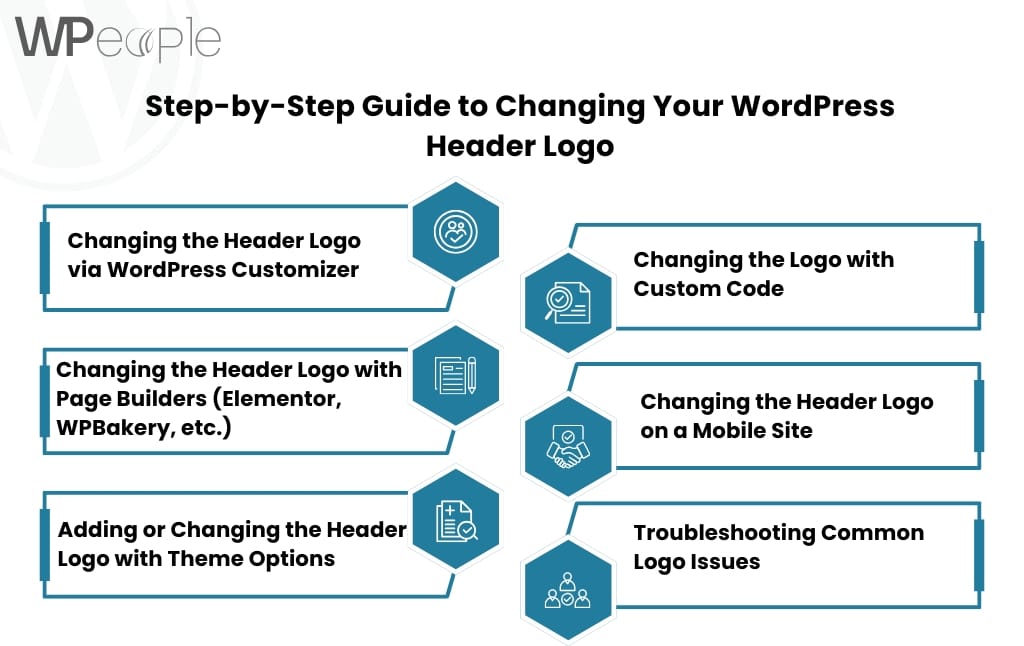
How to Set Up & Customize Your WordPress Theme
After choosing a theme, the next step is installation and customization. WordPress offers easy-to-use tools like Theme Customizer or page builders (Elementor, WPBakery) to make tweaks.
Follow these steps:
- Install the theme via Appearance > Themes.
- Customize it using Appearance > Customize.
- Add content and configure widgets.
For advanced customizations, consider hiring a developer.
When Should You Hire a Developer to Help with Your WordPress Theme?
Signs you need professional help include:
- Complex e-commerce or design needs.
- Customization requirements beyond your skill level.
- Performance or speed issues.
A developer can save time and ensure everything works perfectly.
Conclusion
Selecting the right WordPress theme is a combination of aesthetics, functionality, and SEO performance & compatibility. Taking the time to research, demo-test, and choose carefully can save you technical headaches in the future.
Explore themes carefully or contact a professional for expert guidance if needed. Your website’s success depends on the foundation you lay today!
FAQs
What is the difference between a free and premium WordPress theme?
Free WordPress Themes:
Free themes are available in the WordPress Theme Repository and are generally easy to install and use. They’re great for simple websites and small businesses on a budget.
Pros of Free Themes:
- They are free of charge.
- Quick to set up and install.
- Good for basic websites or personal projects.
Cons of Free Themes:
- Limited design and customization options.
- Often lack advanced features.
- May not have dedicated customer support.
Premium WordPress Themes:
Premium themes are paid and typically offer advanced design features, better performance, and dedicated support.
Pros of Premium Themes:
- Advanced design and customization options.
- Dedicated customer support and updates.
- Built with additional features like SEO optimization and integration with popular plugins.
Cons of Premium Themes:
- They cost money (usually a one-time or annual fee).
When to Choose Premium Themes:
If you want advanced functionality, better customization options, or require dedicated support, investing in a premium theme is worth it.
How can I tell if a WordPress theme is mobile-friendly?
A mobile-friendly theme ensures that your website looks and functions well on all devices, including smartphones, tablets, and desktops. Here’s how to check if a WordPress theme is mobile-friendly:
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test Tool:
Input the theme demo URL into Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. This will indicate if the site is optimized for mobile viewing. - Test it Manually:
Resize your browser window to simulate mobile devices, or open the demo on different mobile devices. - Check Responsiveness Features:
A responsive theme will adjust menus, text, and layouts automatically as per screen size. - Look at Theme Descriptions:
Most WordPress themes explicitly mention responsiveness as a feature if they are mobile-friendly.
How much customization do WordPress themes allow?
The amount of customization varies depending on the WordPress theme you choose:
- Free Themes:
Generally allow basic adjustments like logo uploads, color changes, and simple widget placements. - Premium Themes:
Premium themes come with advanced customization options, including options via the WordPress Customizer, built-in page builders (Elementor, WPBakery, etc.), or custom settings. - Theme Builders & Plugins:
Tools like Elementor or the WordPress Theme Customizer allow you to tweak design elements like font styles, colors, layout, and more.
For advanced changes like custom CSS, hiring a developer may be necessary unless you have coding knowledge.
Can I change my WordPress theme after my website has gone live?
Yes, you can change your WordPress theme at any time, even after your website has gone live. However, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Content and Formatting: Changing a theme may affect how your content is displayed, as themes have different templates. Double-check everything after switching themes.
- Backup Your Website: Always backup your website before switching themes to ensure you can revert changes if something goes wrong.
- Test on a Staging Site: If possible, test the new theme on a staging environment before applying changes to your live website.
What are the best WordPress theme marketplaces?
There are several popular marketplaces where you can find both free and premium WordPress themes. Here are some trusted options:
- ThemeForest: One of the largest marketplaces for premium WordPress themes. You’ll find thousands of options for every niche here.
- Elegant Themes: Known for the Divi Builder and well-crafted themes. Ideal for multipurpose sites.
- StudioPress: Home of the Genesis Framework, great for developers and minimalistic designs.
- TemplateMonster: Offers a wide range of premium themes and pre-built website templates.
- MOJO Marketplace: A great choice for beginners and small businesses.
These marketplaces are excellent resources to find professional, well-coded WordPress themes suited for different purposes.
How do I know if a WordPress theme is SEO optimized?
An SEO-optimized WordP ress theme improves your chances of ranking higher in search engine results. Look for the following signs to determine if a theme is SEO-optimized:
- Speed and Performance:
Fast-loading themes are better optimized for SEO. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to test performance. - Schema Markup Support:
Schema markup allows search engines to better understand your content. Most SEO-optimized themes integrate schema markup. - Clean, Lightweight Code:
Well-coded themes load faster and are easier for search engines to index. - Responsive Design:
Mobile-friendly and responsive themes rank higher in mobile search results. - Compatibility with SEO Plugins:
Look for themes that integrate seamlessly with SEO plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math.
Do I need technical skills to change or customize a WordPress theme?
You do not necessarily need advanced technical skills to customize a WordPress theme.
- Beginner-Friendly Customizations:
- Changing colors and logos using the WordPress Customizer.
- Adjusting basic layout options or widgets.
- Intermediate Skills:
- Using page builders like Elementor or WPBakery.
- Advanced Customization:
- Editing CSS or creating custom templates requires coding knowledge.
- Hiring a developer is recommended if you lack these skills.
WordPress offers a balance of intuitive tools and advanced customization options, catering to users of all technical levels.
Why is theme performance important for my WordPress website?
Theme performance plays a key role in user experience and SEO rankings. A poorly coded or heavy WordPress theme can lead to slow load times, which can frustrate users and increase bounce rates.
Why Theme Performance Matters:
- Improved User Experience: Faster websites are easier for users to navigate and engage with.
- Better SEO Rankings: Google prioritizes speed as a ranking factor.
- Reduced Bounce Rates: Users are more likely to leave if a site takes too long to load.
How to Improve Theme Performance:
- Choose lightweight themes.
- Optimize images and media.
- Use caching plugins.
- Avoid feature overload and unnecessary widgets.
By ensuring your theme is optimized for speed, you’re giving your visitors and search engines a better experience.