
Have you noticed your WordPress site feeling sluggish lately? Pages taking longer to load? Your hosting provider warning about resource usage? Before you blame your theme or start uninstalling plugins randomly, there’s a hidden culprit you might not have considered: WordPress Cron jobs.
Most WordPress site owners don’t even know what WP-Cron is, let alone that it could be the reason their site feels like it’s running through mud. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover how WordPress handles scheduled tasks, why it can become a performance nightmare, and most importantly how to fix it.
The Hidden Performance Killer: Understanding WP-Cron
WordPress runs scheduled tasks differently than you might expect. Every time someone visits your website, every single visitWordPress checks if there are any scheduled tasks that need to run. This system is called WP-Cron.
What Makes WP-Cron Different (and Problematic)?
Unlike traditional server cron jobs that run at specific times regardless of website traffic, WP-Cron only triggers when someone loads a page on your site. Think of it like a lazy employee who only starts working when the boss walks by.
Here’s what happens behind the scenes:
- A visitor lands on your homepage
- WordPress loads all its core files
- Before displaying the page, it checks: “Are there any cron jobs due?”
- If yes, it spawns a background process to run those tasks
- Only then does it serve the page to your visitor
This process adds overhead to every single page load. On a high-traffic site, that means thousands of unnecessary checks every hour.
The Technical Reality: Why WordPress Chose This Approach
WordPress was designed to work on any hosting environment, including basic shared hosting where users don’t have access to server-level cron jobs. The WP-Cron system was a clever workaround that made WordPress incredibly portable and easy to install anywhere.
When WordPress was first developed in 2003, most websites were small blogs with minimal traffic. The performance overhead was negligible. Fast forward to today, and WordPress powers 43% of all websites, including massive e-commerce stores, news sites, and enterprise applications. The same system that worked fine for a personal blog now becomes a bottleneck for business-critical applications.
Why This Matters for Your Business
If you’re running an e-commerce store, a membership site, or any business-critical WordPress installation, these milliseconds add up. Studies show that:
- A 1-second delay in page load time can reduce conversions by 7%
- 40% of visitors abandon a site that takes more than 3 seconds to load
- Google considers page speed as a ranking factor for both desktop and mobile search
- 53% of mobile users leave a site that takes longer than 3 seconds to load
When WP-Cron runs heavy tasks like generating reports, sending bulk emails, or processing data it can delay page rendering for your actual visitors. That’s a direct hit to your revenue and search rankings.
The Anatomy of WP-Cron: What’s Really Happening
To truly understand the performance impact, let’s dive deeper into the mechanics of WP-Cron execution.
The Page Load Sequence
When a typical WordPress page loads with WP-Cron enabled:
Step 1 (0-50ms): Initial HTTP request received
Step 2 (50-200ms): WordPress core loads, database connection established
Step 3 (200-250ms): WP-Cron check initiates – queries database for scheduled events
Step 4 (250-300ms): If cron jobs are due, spawns background HTTP request to itself
Step 5 (300ms+): Page continues rendering while cron jobs execute in parallel
The problem? That “parallel” execution isn’t truly parallel on many hosting environments. On shared hosting or servers with limited resources, the cron execution competes with page rendering for CPU and memory. This creates visible slowdowns.
The Multiplier Effect
Here’s what makes it worse: if five visitors load your site simultaneously, WordPress potentially spawns five separate cron checks. While WordPress has logic to prevent duplicate execution, the checking process itself consumes resources.
On a site receiving 100 visits per hour, that’s 100 database queries checking for scheduled tasks, even if there’s nothing scheduled to run. For a high-traffic site with 10,000 visits per hour, that’s 10,000 unnecessary database queries every single hour.
The Hidden Cron Jobs You Don’t Know About
Most site owners think cron jobs are just for scheduled posts. In reality, WordPress and your plugins create dozens of background tasks:
WordPress Core Tasks:
- Checking for WordPress updates (twice daily)
- Checking for plugin updates (twice daily)
- Checking for theme updates (twice daily)
- Cleaning up old transients from database (daily)
- Purging expired comments from trash (daily)
- Regenerating .htaccess file (weekly on some configurations)
Common Plugin Tasks:
- Backup plugins: Full site backups, incremental backups, database exports
- SEO plugins: Sitemap generation, broken link checking, analytics syncing
- Security plugins: Malware scanning, login attempt monitoring, database hardening
- Cache plugins: Cache preloading, cache cleanup, optimization routines
- Email plugins: Queue processing, bounce handling, list cleaning
- Analytics plugins: Data aggregation, report generation, API syncing
- Social media plugins: Auto-posting, metrics collection, feed updates
- E-commerce plugins: Inventory syncing, abandoned cart emails, report generation
We’ve audited sites with over 60 active cron jobs running throughout the day. Each one adds overhead.
The 5 Warning Signs WP-Cron Is Hurting Your Site
How do you know if WP-Cron is causing problems? Look for these telltale signs:
1. Inconsistent Page Load Times
Some pages load quickly, while others take several seconds. This inconsistency often occurs because certain page loads trigger cron jobs while others don’t. Run multiple speed tests at different times if you see load times varying by more than 500ms without traffic changes, WP-Cron interference is likely.
2. Spike in Server Resource Usage
Your hosting provider sends warnings about CPU or memory limits, especially during peak traffic hours. WP-Cron tasks competing with regular traffic can max out your server resources. Check your server logs you’ll often see simultaneous spikes in CPU usage and wp-cron.php execution.
3. Scheduled Posts Publishing Late
You schedule a blog post for 9:00 AM, but it doesn’t go live until 9:47 AM when someone finally visits your site. This unpredictability is classic WP-Cron behavior. For content marketing teams running time-sensitive campaigns, this unreliability is unacceptable.
4. Plugin Tasks Not Running Reliably
Backup plugins, SEO tools, and analytics plugins rely on cron jobs. If your backups are inconsistent or your automated tasks keep failing, WP-Cron might be the culprit. We’ve seen cases where nightly backups failed for weeks because the site received no traffic during the scheduled backup window.
5. Slow Admin Dashboard
The WordPress admin area feels sluggish, especially when checking scheduled posts or viewing plugin settings. This can indicate cron job congestion. The admin dashboard itself can trigger cron checks, making routine tasks frustratingly slow.
The Real Cost of Ignoring This Problem
Beyond just slow loading speeds, poorly configured cron jobs can create cascading problems:
Business Impact:
- Lost sales from abandoned carts due to slow checkouts (average cart value × abandonment rate = quantifiable loss)
- Reduced email deliverability if your email queue backs up (marketing ROI suffers)
- Missed marketing opportunities when scheduled campaigns don’t deploy on time
- Poor user experience leading to decreased customer retention and lifetime value
- Damaged brand reputation from a “laggy” website
- Lower search rankings due to poor Core Web Vitals scores
Technical Debt:
- Increased server costs as you upgrade hosting to compensate (often $50-300/month more than needed)
- Plugin conflicts and errors from failed scheduled tasks
- Database bloat from stuck or failed cron events that pile up over time
- Difficulty scaling your site as traffic grows
- Increased complexity troubleshooting other issues when cron problems create false flags
Real-World Financial Impact:
Consider a mid-sized e-commerce site generating $50,000 monthly revenue:
- 2% conversion rate on 25,000 monthly visitors
- 40% of mobile users experience slow loads during cron execution
- Average order value: $100
If page delays from WP-Cron cause just a 10% drop in mobile conversions during affected loads, that’s approximately $2,000 in lost monthly revenue,$24,000 annually. Many site owners throw money at hosting upgrades when a one-time $500-1,500 optimization would solve their performance issues permanently.
The Professional Solution: Disabling WP-Cron the Right Way
The most effective fix is disabling WP-Cron and replacing it with proper server-side cron jobs. However, this isn’t as simple as flipping a switch; it requires careful implementation to avoid breaking your site.
Step 1: Audit Your Current Cron Jobs
Before making changes, you need to know what’s currently scheduled. This discovery phase is critical and often reveals surprises.
Manual Audit Using Plugins:
Install a plugin like “WP Crontrol” or “Advanced Cron Manager” to view all scheduled tasks. Document:
- Event name (hook)
- Recurrence interval
- Next scheduled run time
- Which plugin/theme created it
- Arguments passed to the event
You might be surprised to find dozens of jobs you didn’t know existed. We routinely find abandoned cron jobs from deleted plugins still running years later, consuming resources for no reason.
Database-Level Investigation:
For a complete picture, examine the wp_options table directly:
Look for the cron option key. This serialized array contains every scheduled event. Expert developers can parse this to identify problematic patterns like:
- Jobs scheduled to run every minute (excessive)
- Multiple duplicate jobs (configuration errors)
- Jobs with execution times in the past (stuck/failed tasks)
Step 2: Clean Up Before Optimization
Before disabling WP-Cron, clean house:
Remove Unnecessary Jobs:
- Deactivate unused plugins and verify their cron jobs are removed
- Disable update checks if you manage updates manually
- Remove duplicate scheduled events
Optimize Existing Jobs:
- Consolidate similar tasks to run together
- Adjust overly frequent schedules (does that task really need to run every 5 minutes?)
- Stagger resource-intensive tasks to avoid conflicts
This cleanup alone can improve performance by 15-30% without any structural changes.
Step 3: Disable WP-Cron Safely
Add this line to your wp-config.php file (above the “/* That’s all, stop editing! */” line):
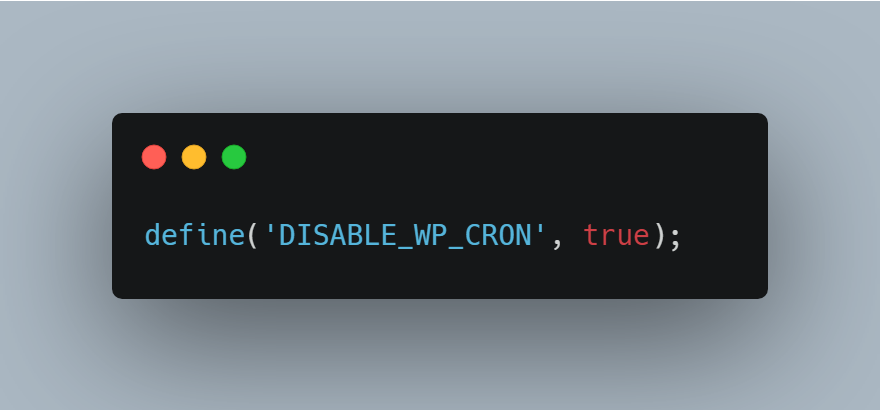
Critical Warning: Once you disable WP-Cron, your scheduled tasks will stop running completely unless you set up a replacement. Don’t do this unless you’re ready to implement Step 4 immediately.
Best Practice: Implement this during a maintenance window or low-traffic period, and have a rollback plan ready.
Step 4: Configure Server-Level Cron Jobs
This is where things get technical. You need to set up your server to trigger wp-cron.php at regular intervals. The exact method depends on your hosting environment:
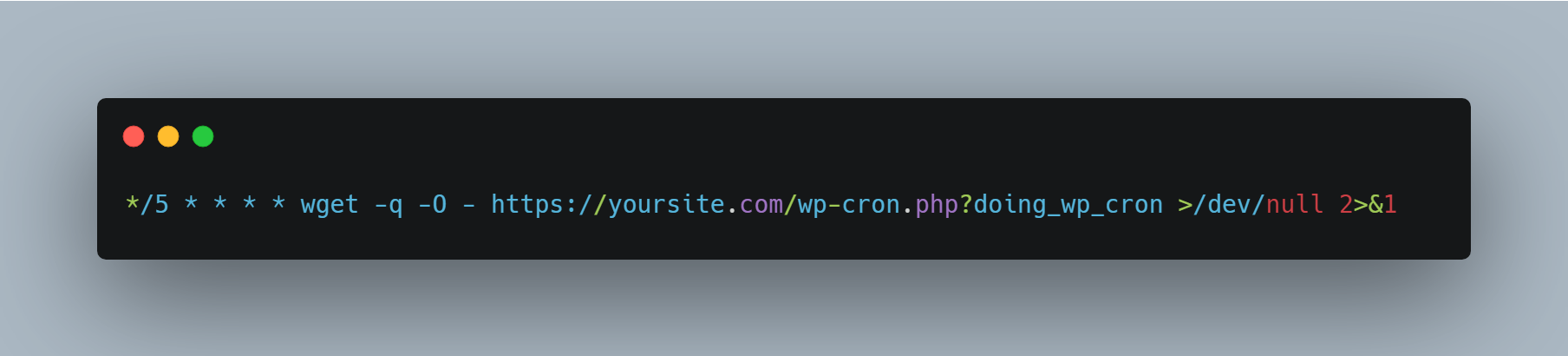
For cPanel Hosting:
Navigate to Advanced → Cron Jobs, then add:
Alternative using curl (faster, if available):
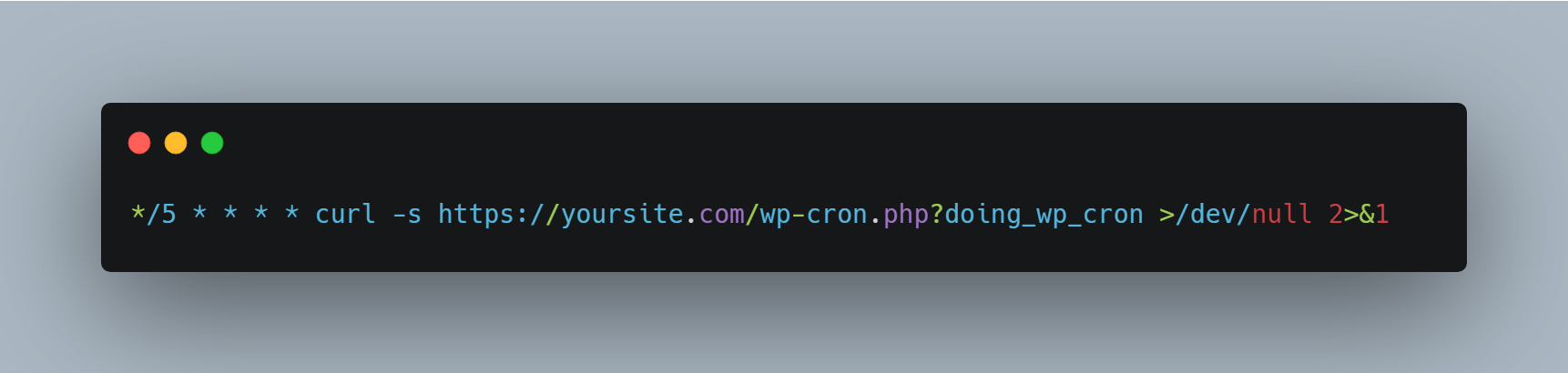
This runs every 5 minutes. For most sites, this interval works well.
Understanding Cron Syntax:
The timing format follows this pattern:
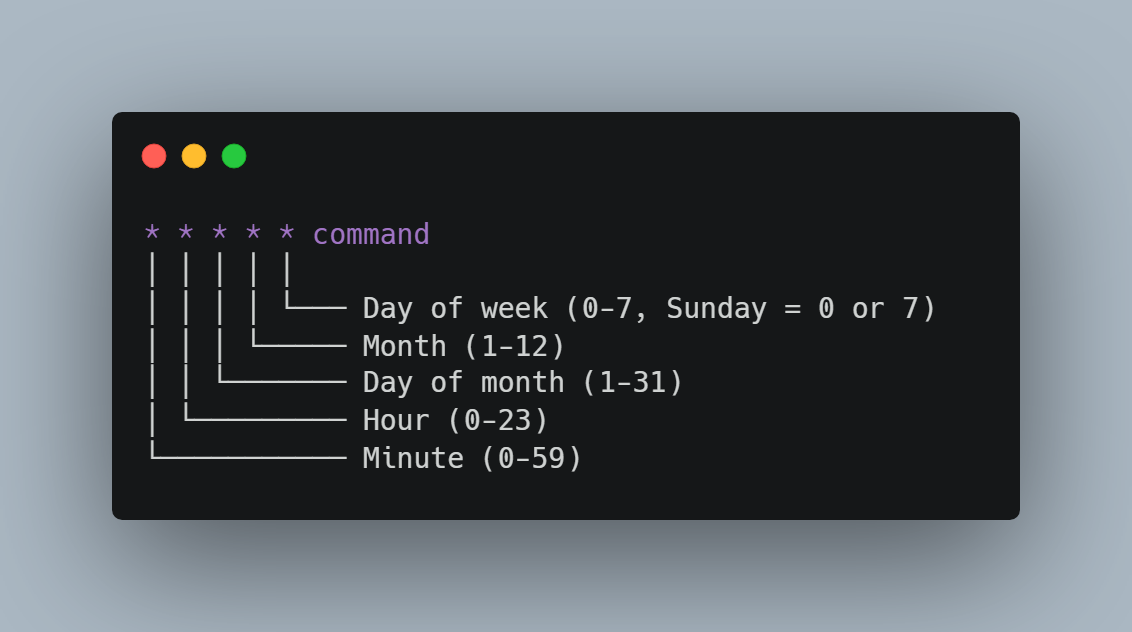
Common intervals:
- */1 * * * * – Every minute (for high-priority sites)
- */5 * * * * – Every 5 minutes (standard recommendation)
- */15 * * * * – Every 15 minutes (low-traffic sites)
- 0 * * * * – Every hour, on the hour
For Managed WordPress Hosting:
Platforms like WP Engine, Kinsta, or Flywheel often have built-in cron management:
- WP Engine: Supports server cron, contact support to enable
- Kinsta: Automatic server-level cron, no configuration needed
- Flywheel: Available on higher plans, contact support
Check their documentation or contact support before making changes.
For VPS or Dedicated Servers:
You’ll need SSH access to edit the crontab directly:
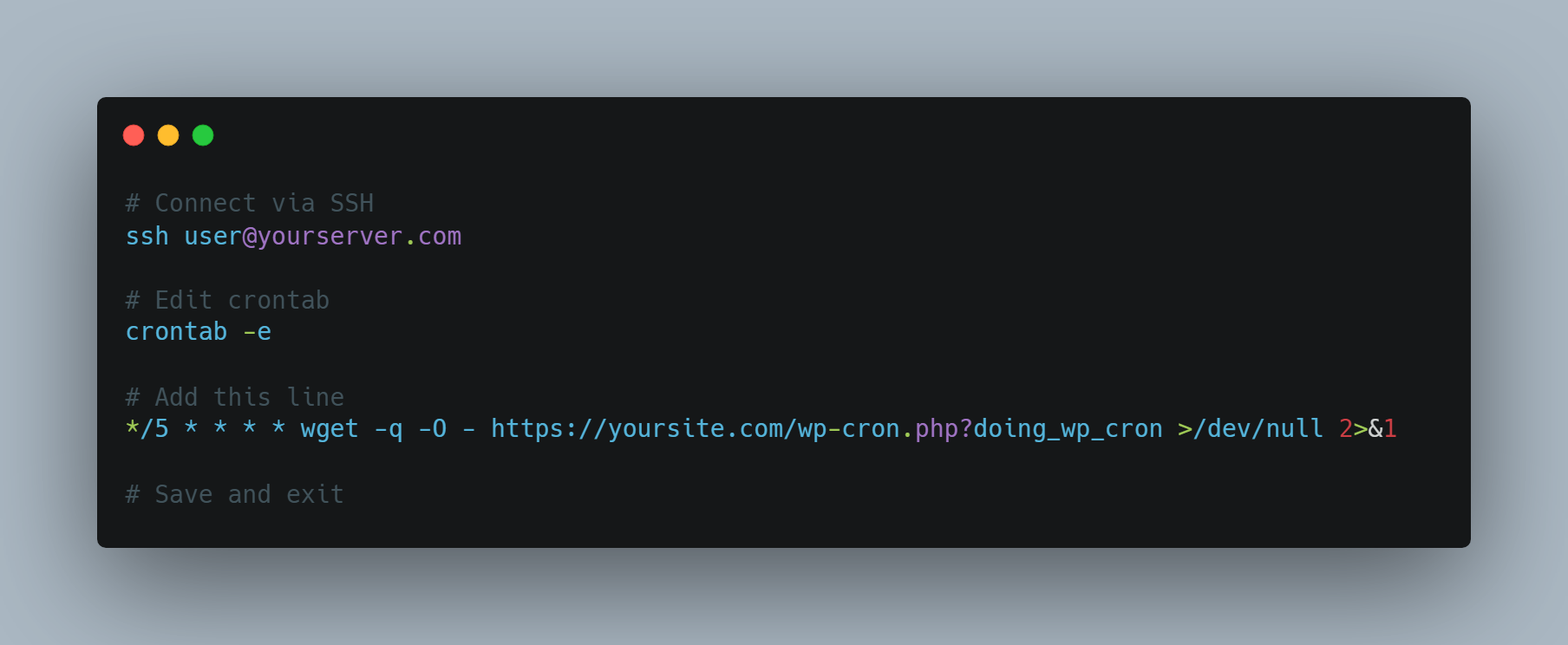
Security Consideration:
For public-facing sites, consider adding authentication to wp-cron.php to prevent unauthorized execution. This requires custom configuration and is part of professional optimization services.
Step 5: Verify Everything Still Works
After implementation, monitor your site for 24-48 hours:
Immediate Checks (First Hour):
- Check that scheduled posts publish on time
- Verify plugin tasks are completed (backups, emails, etc.)
- Review error logs for any cron-related failures
- Test a few critical user workflows (checkout, registration, etc.)
Short-Term Monitoring (24-48 Hours):
- Monitor server resource usage for improvements using tools like New Relic or server monitoring
- Test page load speeds using GTmetrix, Pingdom, or Google PageSpeed Insights
- Check analytics for any anomalies in user behavior
- Verify all automated emails are sent (order confirmations, password resets, etc.)
Performance Metrics to Track:
- Average page load time (should decrease 20-40%)
- Time to First Byte (TTFB) (should improve 15-30%)
- Server CPU usage (should drop 30-50% during peak hours)
- Database query time (should decrease noticeably)
- Bounce rate (should improve if speed was causing exits)
Advanced Optimization: Custom Cron Intervals
Some tasks don’t need to run every 5 minutes. Newsletter processing might only need to run hourly, while critical e-commerce tasks might need to run every minute.
Creating Intelligent Schedules
WordPress defaults to these intervals:
- hourly (once per hour)
- twice daily (twice per day)
- daily (once per day)
- weekly (once per week)
But your business needs might require custom intervals:
E-Commerce Priority Example:
- Every 1 minute: Payment gateway synchronization, inventory updates from suppliers
- Every 5 minutes: Order processing queue, abandoned cart tracking
- Every 15 minutes: Email queue processing, customer notification batches
- Hourly: Sales reports generation, analytics aggregation
- Every 6 hours: Full inventory reconciliation
- Daily: Database optimization, old order archiving, backup verification
Membership Site Example:
- Every 5 minutes: New member onboarding emails
- Every 15 minutes: Access level checking for expired memberships
- Hourly: Engagement metrics calculation
- Daily: Member activity reports, content drip releases
- Weekly: Member retention analysis
The Technical Implementation
Creating custom intervals requires adding code to your theme’s functions.php or a custom plugin:
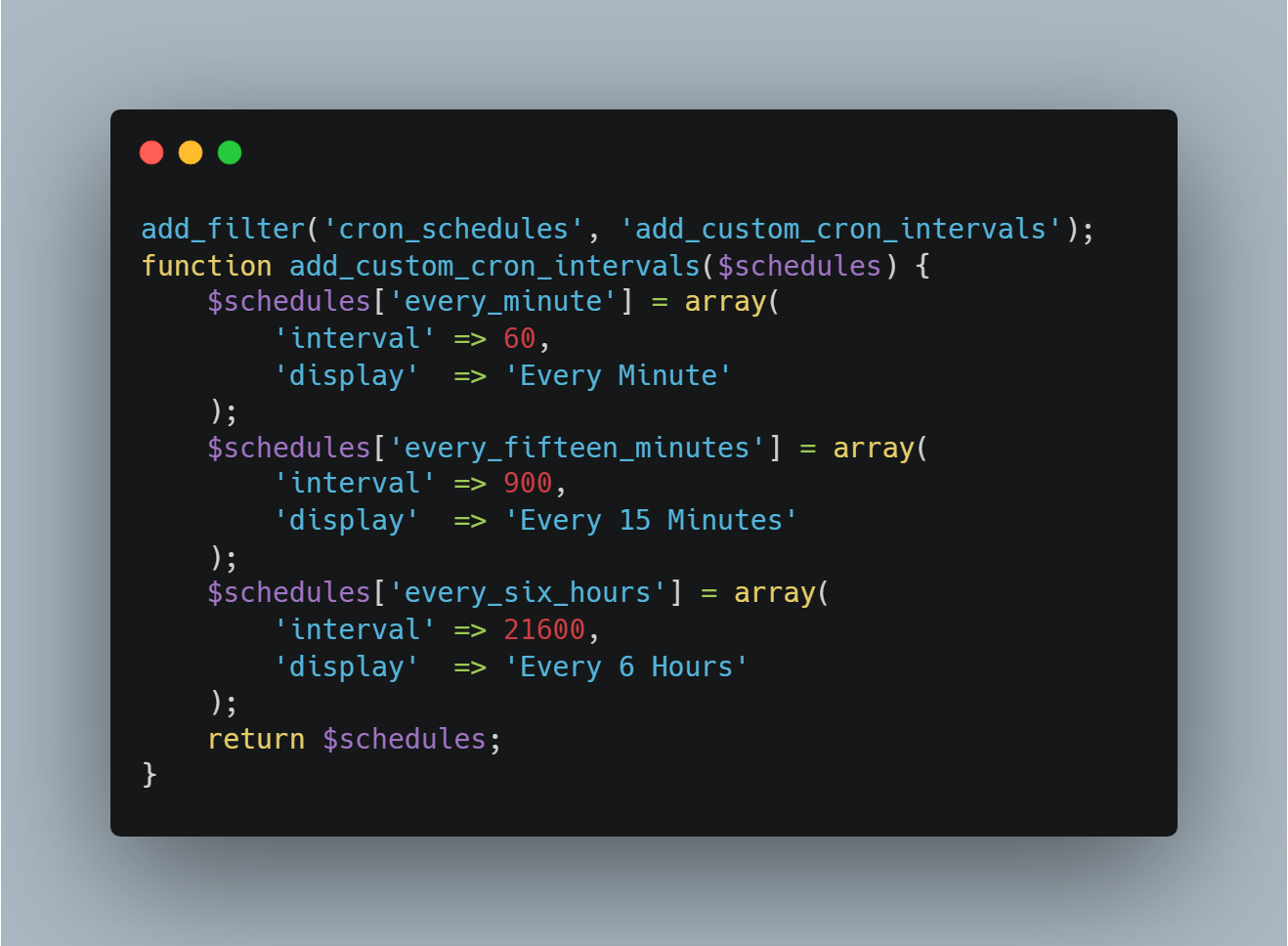
This level of customization requires understanding both WordPress internals and your specific business workflows.
Load Distribution Strategies
Professional implementations go further by staggering tasks to prevent resource conflicts:
- Run heavy database operations during low-traffic hours (typically 2-5 AM local time)
- Distribute email sending throughout the day rather than one large batch
- Offset similar tasks by a few minutes to prevent CPU spikes
- Implement queue systems for tasks that can be processed asynchronously
Why DIY Optimization Often Backfires
We’ve worked with dozens of business owners who tried to implement these fixes themselves. Here’s what typically goes wrong:
Common Mistakes:
- Disabling WP-Cron without a replacement – Scheduled posts stop publishing, backups fail, and plugins break silently. Recovery requires identifying every broken workflow manually.
- Wrong cron syntax – Tasks run too frequently (overloading the server) or not at all. We’ve seen accidental configurations that triggered wp-cron.php every second, bringing servers to their knees.
- Missing error logging – Problems occur silently, and you don’t know until something major breaks. Without proper logging, debugging takes hours instead of minutes.
- Incorrect file paths – The cron job can’t find wp-cron.php and fails repeatedly. This is especially common on sites with unusual directory structures or security configurations.
- Inadequate testing – Everything seems fine initially but breaks under traffic load. Testing with low traffic doesn’t reveal problems that emerge during peak usage.
- Security holes – Leaving wp-cron.php publicly accessible without protection allows potential abuse. Attackers can trigger resource-intensive cron jobs repeatedly.
- Missing multisite considerations – Network-wide cron jobs require special handling that differs from single-site implementations.
Real Disaster Stories
Case Study: The E-Commerce Email Catastrophe
One client came to us after their “optimization” caused their WooCommerce store to stop sending order confirmation emails for three days. They lost sales and customer trust because they didn’t realize their fix had broken a critical function. Customers thought orders weren’t processed, leading to chargebacks and angry phone calls. The recovery included:
- Manually sending 247 order confirmations
- Offering goodwill discounts to affected customers (cost: $3,700)
- Emergency reputation management
- Technical recovery taking 12 hours
Total cost of the DIY mistake: Over $8,000 in lost revenue and recovery expenses.
Case Study: The Membership Site Lockout
A membership site disabled WP-Cron without realizing their access control plugin relied heavily on scheduled checks. When the cron jobs stopped, new members couldn’t access content and renewals didn’t process correctly. They lost 12% of their monthly recurring revenue before discovering the issue five days later.
The Hosting Environment Factor
Not all hosting environments are created equal when it comes to cron optimization.
Shared Hosting Challenges
On shared hosting (GoDaddy, Bluehost, HostGator, etc.):
- Limited control over server configuration
- Resource restrictions affect cron execution
- Other sites on the same server impact performance
- Cron job frequency limits (often max every 15 minutes)
- Some hosts block wp-cron.php completely for security
Recommendation: If you’re on shared hosting and experiencing performance issues, cron optimization provides limited relief. Consider upgrading to VPS or managed WordPress hosting for serious business sites.
VPS and Dedicated Server Advantages
Full server control enables:
- Precise cron timing down to the second
- Resource allocation specifically for cron jobs
- Advanced scheduling with job dependencies
- Complete logging and monitoring
- Security lockdown of cron execution
Cloud Hosting Considerations (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure)
Cloud environments offer the most flexibility:
- Separate workers for cron processing
- Auto-scaling based on job queue depth
- Geographic distribution for global audiences
- Advanced queuing systems (AWS SQS, Google Cloud Tasks)
- Serverless cron alternatives (AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions)
However, this complexity requires DevOps expertise to implement correctly.
The Enterprise Approach: Professional Cron Management
Large-scale WordPress sites use sophisticated cron management strategies that go far beyond basic optimization:
Advanced Architecture Patterns
1. Dedicated Cron Server
Separate application server from cron execution:
- Web servers handle only user requests
- Dedicated cron server processes all scheduled tasks
- Eliminates performance impact on user experience
- Enables resource allocation tuned for batch processing
2. Queue-Based Systems
Replace direct cron execution with job queues:
- Tasks added to queue instead of immediate execution
- Worker processes consume queue at controlled rate
- Automatic retry logic for failed jobs
- Priority queues for critical tasks
- Real-time monitoring of queue depth and processing speed
3. Microservices Architecture
Break cron functionality into independent services:
- Email service handles only email-related cron jobs
- Payment service processes payment-related tasks
- Each service scales independently based on load
- Failure isolation prevents cascading problems
Enterprise Monitoring
Professional implementations include comprehensive monitoring:
Real-Time Dashboards Tracking:
- Cron job execution frequency and duration
- Success/failure rates per job type
- Resource consumption per job
- Queue depth and processing lag
- Cost per job execution (important for cloud environments)
Automated Alerting:
- Instant notification when jobs fail
- Warnings when jobs exceed normal execution time
- Alerts for queue backlog building up
- Capacity warnings before resources max out
Performance Analytics:
- Historical trends showing optimization effectiveness
- Correlation analysis between cron timing and user metrics
- Predictive alerts for potential issues
- Cost optimization recommendations
Load Balancing Strategies
Time-Based Distribution: Intelligent scheduling spreads load throughout the day rather than clustering jobs at arbitrary intervals. For example, instead of all hourly jobs running at the top of the hour (creating a spike), they’re distributed: some at :05, others at :17, others at :33, etc.
Priority Queuing: Critical tasks (like order processing) run before non-essential tasks (like social media posting). If resources are constrained, low-priority jobs queue until capacity is available.
Geographic Distribution: For global sites, cron jobs run on servers geographically closest to the data they’re processing, reducing latency and improving execution speed.
These enterprise solutions require custom development and ongoing management, but they’re essential for sites processing thousands of transactions daily or serving millions of visitors monthly.
Alternative Solutions: When Full Optimization Isn’t Needed
Not every site requires complete WP-Cron replacement. Sometimes simpler solutions work:
The Hybrid Approach
Keep WP-Cron enabled but optimize how it runs:
- Reduce Check Frequency: Modify how often WordPress checks for scheduled events
- External Trigger: Use an uptime monitoring service (like UptimeRobot) to ping wp-cron.php regularly
- Selective Disabling: Disable only for frontend, keep enabled for admin
This provides 60-70% of the performance benefit with less complexity.
Plugin-Based Solutions
Several plugins offer optimization without code changes:
- WP Crontrol: Manages existing cron jobs, helps identify problems
- Disable WP Cron: Simple interface for disabling WP-Cron
- Advanced Cron Manager: Visual management of all scheduled tasks
However, plugins add another layer of code to maintain and can themselves create performance issues.
When to Keep Default WP-Cron
Some sites work fine with default WP-Cron:
- Low-traffic personal blogs (under 100 visitors/day)
- Sites with minimal plugins (less than 10 active)
- Sites without time-critical scheduled tasks
- Staging/development environments
If your site isn’t experiencing performance issues, the complexity of optimization may not be worthwhile.
Real-World Results: What Proper Cron Optimization Achieves
When implemented correctly, cron optimization delivers measurable improvements:
Performance Gains:
- 20-40% reduction in average page load time
- 50-70% decrease in server resource usage during peak hours
- Consistent page load speeds regardless of traffic patterns
- Improved scalability as traffic grows
- Better Core Web Vitals scores affecting SEO rankings
Reliability Improvements:
- Scheduled content publishes exactly on time
- Plugin tasks complete reliably without manual intervention
- Email queues process smoothly without delays or bounces
- Backup and maintenance tasks run predictably
- Zero failed cron jobs from resource exhaustion
Cost Savings:
- Reduced need for hosting upgrades ($50-300/month savings typical)
- Lower server resource consumption (20-40% reduction in CPU/memory)
- Fewer emergency support tickets and crisis management
- Decreased downtime and maintenance needs
- Better resource utilization means delayed infrastructure scaling
Business Impact Examples:
E-Commerce Client (Fashion Retailer):
- Previous state: Cart abandonment 73%, conversion rate 1.8%
- After optimization: Cart abandonment 61%, conversion rate 2.1%
- Result: 12% increase in conversion rate translated to $180,000 additional annual revenue
- Implementation cost: $1,200 one-time
Membership Site (Online Education):
- Previous state: Member complaints about access delays, content not releasing on schedule
- After optimization: Zero access issues, perfect content drip execution
- Result: Churn rate decreased from 8% to 5.5% monthly, retaining $14,400 more in annual recurring revenue
- Implementation cost: $900 one-time
News Publishing Site:
- Previous state: Articles publishing 15-45 minutes late, SEO penalties for poor page speed
- After optimization: Precise publishing, 42% improvement in mobile page speed scores
- Result: 23% increase in organic search traffic within 90 days
- Implementation cost: $1,500 one-time
Security Implications of Cron Optimization
An often-overlooked aspect of cron optimization is security. Improperly configured cron systems create vulnerabilities:
Common Security Risks
1. Unauthenticated wp-cron.php Access
By default, anyone can trigger wp-cron.php by visiting the URL. Attackers can exploit this to:
- Overwhelm your server by repeatedly triggering cron execution
- Time attacks to coincide with cron execution for maximum disruption
- Trigger resource-intensive tasks deliberately to cause downtime
2. Information Disclosure
Cron jobs often process sensitive data:
- Customer emails and personal information
- Financial transaction details
- User access credentials
- Business intelligence and analytics
Poor logging practices can expose this data in plain text log files.
3. Privilege Escalation
Some cron jobs run with elevated privileges. Vulnerabilities in custom cron code can allow attackers to execute unauthorized actions.
Security Best Practices
Implement these protections:
- Restrict wp-cron.php Access: Use server configuration to limit access to wp-cron.php to your server’s IP address only
- Add Authentication: Require a secret token passed as a parameter to wp-cron.php
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Never log passwords, payment details, or personal information
- Use Secure Connections: Always trigger wp-cron.php via HTTPS
- Implement Rate Limiting: Prevent abuse by limiting how frequently wp-cron.php can be accessed
- Regular Audits: Review cron jobs quarterly for abandoned tasks from deleted plugins
Professional optimization includes these security measures by default.
When to Call in the Experts
While technically inclined site owners can implement basic cron optimization, professional help is recommended when:
High-Stakes Scenarios
- Your site processes significant revenue (e-commerce, memberships, bookings, SaaS)
- Any downtime or malfunction directly impacts revenue
- Cart abandonment from performance issues costs real money
- Customer trust depends on reliability
- Time-critical operations (news sites, event platforms, time-sensitive offers)
- Content must publish at exact times for maximum impact
- Coordinated campaigns across multiple channels require precise timing
- Late execution means missed opportunities
- Complex technical environments (VPS, dedicated, cloud hosting with complex configurations)
- Multi-server setups require advanced knowledge
- Load balancers and CDNs add complexity
- Custom security configurations need careful integration
Technical Complexity Indicators
- Multiple plugins with interdependent cron jobs
- Understanding dependencies prevents breaking workflows
- Optimization must consider the entire ecosystem
- Plugin conflicts can be subtle and difficult to debug
- High traffic volumes (1,000+ visitors daily, 10,000+ for optimization necessity)
- Scale introduces problems that don’t exist on small sites
- Concurrent cron execution requires advanced handling
- Resource constraints become critical
- Previous optimization attempts failed or created problems
- Recovery often more complex than initial implementation
- Existing issues may mask underlying problems
- Professional assessment identifies root causes
- Custom cron scheduling needed for specific business workflows
- Off-the-shelf solutions don’t fit unique requirements
- Business logic requires custom development
- Integration with third-party systems adds complexity
- Unique hosting setups (load balanced, multisite networks, enterprise installations)
- Standard approaches don’t work
- Network-wide changes affect multiple sites
- Enterprise compliance and security requirements
The Value Proposition of Professional Service
Professional WordPress developers don’t just disable WP-Cron and set up a basic cron job. They:
- Analyze Your Entire Technical Stack
- Server configuration review
- Database optimization assessment
- Plugin efficiency evaluation
- Theme performance audit
- Identify bottlenecks beyond just cron
- Implement Intelligent Scheduling
- Custom intervals matched to business needs
- Load distribution for optimal performance
- Priority queuing for critical tasks
- Geographic optimization for global sites
- Ensure Reliability
- Comprehensive testing before deployment
- Fallback mechanisms for failures
- Monitoring and alerting systems
- Documentation for future maintenance
- Provide Ongoing Support
- Performance monitoring post-implementation
- Optimization as your site grows
- Emergency support if issues arise
- Regular audits and recommendations
- Deliver Measurable Results
- Benchmarking before and after
- Clear metrics showing improvement
- ROI calculation demonstrating value
- Ongoing optimization recommendations
The investment in professional optimization typically pays for itself within 1-3 months through improved conversions, reduced hosting costs, or eliminated emergency support needs.
Beyond Cron: The Bigger Performance Picture
Cron optimization is often just one piece of the performance puzzle. A truly fast WordPress site requires addressing multiple factors simultaneously:
Database Optimization
Your database grows over time, becoming sluggish:
- Post revisions accumulating (thousands of old versions)
- Transients never cleaned up (expired data lingering)
- Comment spam in trash but not deleted
- Orphaned metadata from deleted posts
- Unused tables from old plugins
Professional database optimization can reduce query time by 40-60%, directly improving every page load.
Caching Strategy
Multi-layered caching provides dramatic improvements:
- Object Cache (Redis or Memcached): Stores database query results
- Page Cache: Serves pre-generated HTML for common pages
- CDN (Content Delivery Network): Distributes static assets globally
- Browser Cache: Tells browsers to store assets locally
- Opcode Cache: Caches compiled PHP for faster execution
Proper caching can reduce page load time by 70-90% for repeat visitors.
Image Optimization
Images are often the heaviest page elements:
- Unnecessary resolution (serving 4K images when 1080p suffices)
- Uncompressed formats (PNG when JPG would work)
- Missing next-gen formats (WebP offers 30% smaller files)
- Loading all images upfront (lazy loading defers offscreen images)
Image optimization typically reduces page weight by 40-70%.
Code-Level Performance
Clean, efficient code matters:
- Removing unused CSS and JavaScript (often 50%+ of loaded code is unused)
- Minifying remaining code (reducing file size by 20-40%)
- Deferring non-critical JavaScript (allowing page to render faster)
- Optimizing database queries (reducing query count and complexity)
- Eliminating plugin bloat (each plugin adds overhead)
Server Configuration
Proper server setup makes everything faster:
- PHP Version: PHP 8.x is 2-3x faster than PHP 7.x
- HTTP/2 or HTTP/3: Allows parallel resource loading
- GZIP/Brotli Compression: Reduces transfer size by 60-80%
- Resource Limits: Adequate memory and CPU allocation
- Database Configuration: Proper MySQL/MariaDB tuning
The Holistic Approach
Many site owners chase individual fixes without understanding how all these elements interact:
- Caching without image optimization means caching huge pages
- Database optimization without caching means repeated slow queries
- Code optimization without proper server configuration limits gains
- Cron optimization without addressing plugin bloat provides partial improvement
That’s why a holistic approach analyzing your entire WordPress installation and implementing targeted improvements across all layers delivers the best results. A comprehensive audit identifies the specific bottlenecks affecting your site, rather than applying generic optimizations that may or may not help.
Monitoring and Maintaining Optimized Performance
Optimization isn’t a one-time task. Your site evolves, and performance can degrade over time without proper monitoring:
What to Monitor Regularly
Weekly Checks:
- Page load speed trends (using GTmetrix or similar)
- Server resource usage patterns
- Cron job execution logs for failures
- Error logs for new issues
Monthly Reviews:
- New plugins added and their cron jobs
- Traffic pattern changes affecting resource needs
- Hosting resource utilization trends
- User experience metrics (bounce rate, time on site)
Quarterly Audits:
- Comprehensive performance testing
- Database cleanup and optimization
- Plugin necessity review (remove unused)
- Security vulnerability assessment
- Cron job efficiency review
Tools for Ongoing Monitoring
Free Tools:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Core Web Vitals tracking
- GTmetrix: Detailed performance analysis
- Pingdom: Uptime and speed monitoring
- Query Monitor (WordPress plugin): Database query analysis
- WP Crontrol: Cron job management and monitoring
Professional Tools:
- New Relic: Application performance monitoring
- Datadog: Infrastructure and application metrics
- Sentry: Error tracking and debugging
- Cloudflare: CDN with built-in analytics
- ManageWP: Multi-site monitoring dashboard
Performance Degradation Warning Signs
Watch for these indicators that optimization is degrading:
- Gradual Speed Decline: Load times creeping up week over week
- Increasing Server Alerts: More frequent resource warnings from host
- Cron Job Failures: Tasks missing scheduled execution windows
- Growing Database: Significant size increases without content growth
- Plugin Conflicts: New errors appearing in logs
- User Complaints: Reports of slow loading or timeout errors
Early detection prevents small issues from becoming major problems.
The Migration Advantage: Starting Fresh
Sometimes the most effective optimization happens during a migration:
When Migration Makes Sense
Consider migrating to a new hosting environment or fresh WordPress installation when:
- Your current host lacks necessary cron configuration options
- Years of accumulated technical debt make cleanup impractical
- Moving to managed WordPress hosting with built-in optimizations
- Scaling up from shared to VPS/dedicated hosting
- Transitioning to cloud infrastructure for better performance
Migration Best Practices
Pre-Migration Planning:
- Document all current cron jobs and their purposes
- Audit plugins and themes for necessity
- Plan the new architecture with optimization built-in
- Test the migration process in a staging environment
- Prepare rollback procedures in case of issues
During Migration:
- Clean database before transferring (remove old data, optimize tables)
- Transfer only essential plugins and themes
- Implement proper caching from day one
- Configure server-level cron immediately
- Set up monitoring tools before going live
Post-Migration:
- Verify all cron jobs executing correctly
- Test all critical user workflows
- Monitor performance metrics closely for 72 hours
- Document the new configuration for future reference
- Update disaster recovery and backup procedures
A well-executed migration with optimization built-in often provides better results than trying to optimize a site with years of accumulated issues.
Common Myths About WordPress Performance
Let’s dispel some misconceptions that lead site owners astray:
Myth 1: “More RAM/CPU Always Solves Performance Problems”
Reality: Throwing hardware at software problems rarely works. We’ve seen sites on 16GB RAM servers performing worse than optimized sites on 2GB servers. Efficiency matters more than raw power.
Myth 2: “Premium Hosting Automatically Means Fast Sites”
Reality: Expensive hosting provides better infrastructure, but poorly configured WordPress still runs slowly. You need both good hosting AND proper optimization.
Myth 3: “Fewer Plugins Always Means Better Performance”
Reality: One poorly coded plugin can cause more problems than ten well-optimized ones. Quality matters more than quantity. A single plugin that runs 50 database queries per page load does more damage than five plugins that cache intelligently.
Myth 4: “Caching Plugins Solve Everything”
Reality: Caching helps tremendously, but it can’t fix underlying inefficiencies. It’s putting a bandaid on the symptom rather than curing the disease. You need both caching AND optimization for optimal performance.
Myth 5: “Disabling WP-Cron Always Improves Performance”
Reality: Improperly configured server cron can actually perform worse than default WP-Cron in some scenarios. The implementation quality matters more than the approach itself.
Myth 6: “Performance Only Matters for High-Traffic Sites”
Reality: Even small sites benefit from optimization. Better performance means better user experience, improved SEO, lower hosting costs, and professional credibility regardless of traffic volume.
Special Considerations for Different Site Types
Different WordPress applications have unique cron optimization needs:
E-Commerce Sites (WooCommerce, Easy Digital Downloads)
Critical Cron Jobs:
- Order processing and status updates (every 1-5 minutes)
- Inventory synchronization with suppliers (every 5-15 minutes)
- Abandoned cart recovery emails (every 15-30 minutes)
- Payment gateway reconciliation (hourly)
- Sales reporting and analytics (hourly/daily)
Optimization Priorities:
- Never let cron delays impact checkout performance
- Separate order processing from marketing tasks
- Implement queue systems for email sending
- Real-time inventory updates for critical products
- Monitor closely during high-traffic periods (sales, holidays)
Membership and LMS Sites (LearnDash, MemberPress, Restrict Content Pro)
Critical Cron Jobs:
- Access control checks and updates (every 5-15 minutes)
- Content drip scheduling (hourly or daily)
- Subscription renewal processing (daily)
- Engagement tracking and analytics (hourly)
- Email notifications for courses and content (every 15-30 minutes)
Optimization Priorities:
- Precise timing for content releases
- Reliable subscription processing (revenue impact)
- Smooth onboarding experiences for new members
- Efficient access control without impacting page loads
Content Publishing Sites (News, Blogs, Magazines)
Critical Cron Jobs:
- Scheduled post publishing (every 1-5 minutes for precise timing)
- Social media auto-posting (every 15-30 minutes)
- RSS feed generation (every 15-30 minutes)
- Related content calculation (hourly)
- Search index updates (hourly)
- Analytics aggregation (hourly/daily)
Optimization Priorities:
- Exact publish timing for news and time-sensitive content
- Fast RSS updates for subscribers
- Efficient social media integration
- Quick search index updates for new content
Service-Based and Local Business Sites
Critical Cron Jobs:
- Contact form submissions processing (every 5-15 minutes)
- Appointment reminder emails (hourly/daily)
- Backup scheduling (daily)
- Update checks (weekly)
Optimization Priorities:
- Reliable form processing for lead generation
- Consistent backup execution
- Minimal overhead since traffic is typically lower
Each site type benefits from customized cron scheduling aligned with business priorities.
Future-Proofing Your WordPress Performance
Technology evolves, and your optimization strategy should too:
Emerging Trends to Watch
1. Serverless Architecture
Cloud platforms increasingly offer serverless cron alternatives:
- AWS Lambda for scheduled tasks
- Google Cloud Functions for event-driven processing
- Azure Functions for automated workflows
These eliminate traditional server management entirely, automatically scaling based on demand.
2. JAMstack and Headless WordPress
Decoupling WordPress from frontend delivery:
- WordPress as content management only
- Static site generation for faster delivery
- API-driven content updates
- Scheduled builds triggered by cron jobs
This architecture naturally separates cron execution from user experience.
3. Advanced Caching Technologies
Next-generation caching moving beyond traditional approaches:
- Edge computing pushing cache closer to users
- Intelligent cache warming predicting needed content
- Real-time cache invalidation for instant updates
- Machine learning optimizing cache strategies
4. HTTP/3 and QUIC Protocol
New protocols improving connection efficiency:
- Faster initial connections
- Better handling of packet loss
- Improved multiplexing
- Enhanced mobile performance
While not directly related to cron, these technologies complement optimization efforts.
Preparing for WordPress Evolution
WordPress continues evolving, and optimization strategies must adapt:
- Block Editor Impact: Full Site Editing changes how content renders, affecting performance patterns
- PHP Requirements: Newer PHP versions offer performance gains but require testing
- Security Updates: Core updates sometimes change how cron works
- Plugin Ecosystem: Popular plugins evolve, potentially changing cron requirements
Stay informed about WordPress development to adapt optimization strategies proactively rather than reactively.
Conclusion: Performance as a Competitive Advantage
In today’s digital landscape, website performance isn’t a luxury, it’s a competitive necessity. When two businesses offer similar products or services, the faster website wins. When search engines compare similar content, the faster site ranks higher. And when users have multiple options, the smoother experience captures their attention and trust.
Optimizing WordPress cron jobs is a powerful step toward better performance, but it works best as part of a comprehensive, custom WordPress development strategy. The most successful businesses treat performance not as a one-time fix, but as an ongoing investment continuously refining their website’s speed, reliability, and user experience to stay ahead in the digital race.
Consult with Our WordPress Experts On:
- WooCommerce Store
- Plugin Development
- Support & maintenance




